Abstract
Key Contributions
-
We advance the domain of autonomic computing for microservice management through an LLM-based multi-agent framework. To the best of our knowledge, we are the first research work to explore microservice self-management using LLM-based agents.
-
We establish a taxonomy consisting of five levels for autonomous service maintenance. We also present an online evaluation benchmark designed to assess tasks corresponding to each level of autonomy within the microservice demo project Sock Shop.
-
We conduct a rigorous evaluation of our LLM-based microservice management framework using the aforementioned benchmark.
Main Ideas
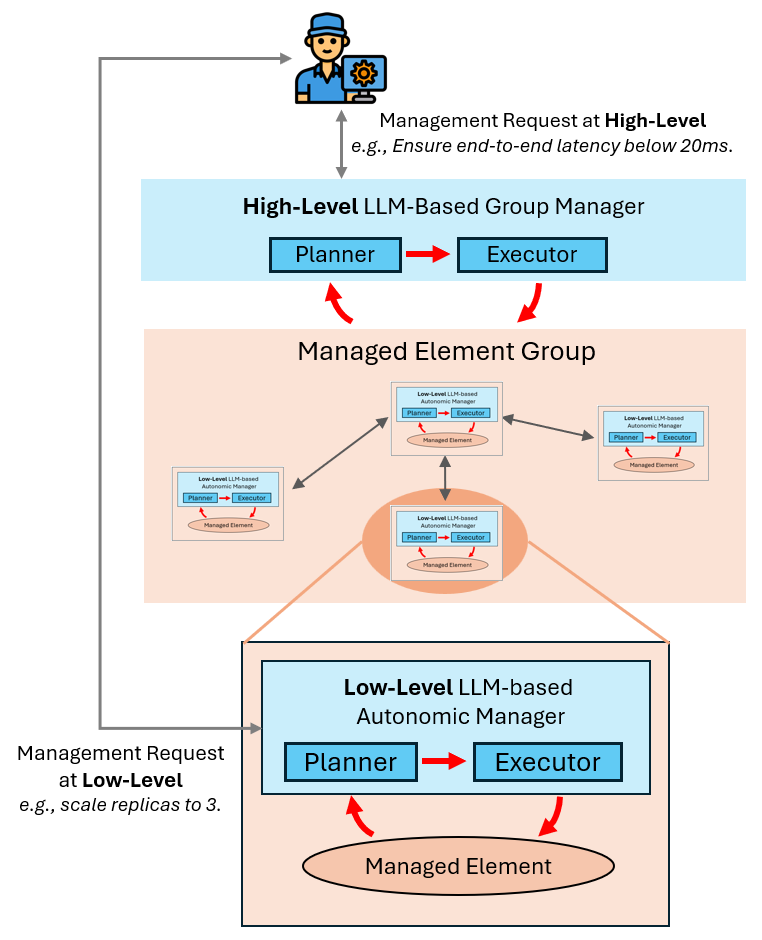
Figure 1: Hierarchical service management framework with LLM-based multi-agent design.
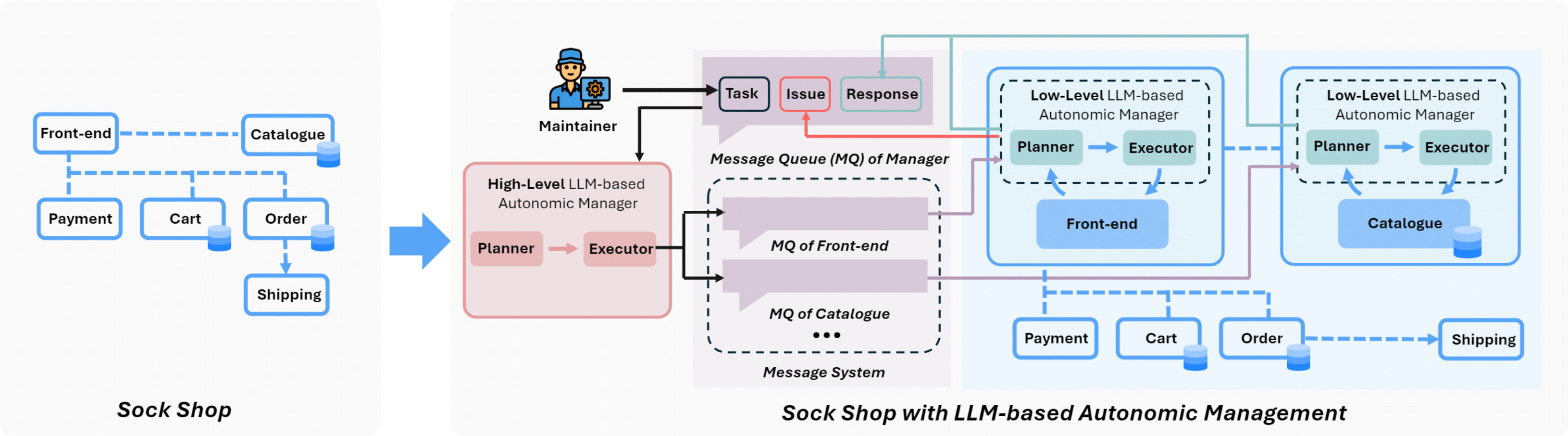
Figure 2: Illustration of the Sock Shop example: Each microservice is converted into an LLM-based autonomic agent, managed by an autonomic layer comprising a Planner and Executor. The high-level group manager employs a Plan-Execute feedback mechanism to generate plans and assign sub-tasks to low-level autonomic agents. A decoupled message queue system serves as the middleware to manage communication, collecting feedback and unresolved issues.
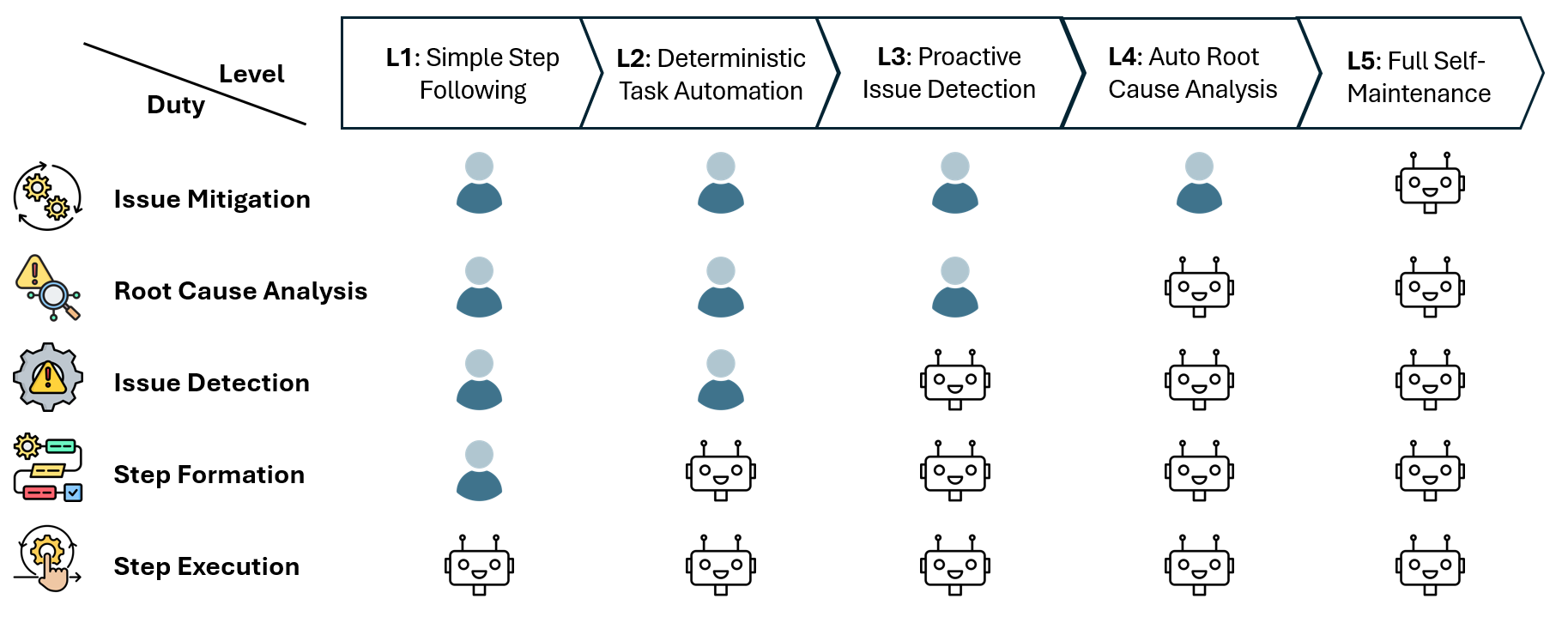
Figure 3: Taxonomy of autonomous levels in service maintenance, focusing on Self-Healing and Self-Optimization.
Citation
@misc{zhang2024visionautonomiccomputingllms,
title={The Vision of Autonomic Computing: Can LLMs Make It a Reality?},
author={Zhiyang Zhang and Fangkai Yang and Xiaoting Qin and Jue Zhang and Qingwei Lin and Gong Cheng and Dongmei Zhang and Saravan Rajmohan and Qi Zhang},
year={2024},
eprint={2407.14402},
archivePrefix={arXiv},
primaryClass={cs.AI},
url={https://arxiv.org/abs/2407.14402},
}